You are viewing this post: วิธีหาเงินโดยที่ไม่ต้องทำงานไปตลอดชีวิต สไตล์ Rich Dad by Robert Kiyosaki | balance sheet แปลว่า
Table of Contents
วิธีหาเงินโดยที่ไม่ต้องทำงานไปตลอดชีวิต สไตล์ Rich Dad by Robert Kiyosaki
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูความรู้เพิ่มเติมที่นี่
Robert Kiyosaki เจ้าพ่อนักลงทุน, อสังหาริมทรัพย์และเจ้าของผลงานเขียนซีรี่ย์ชื่อดัง Rich Dad Poor Dad ได้สอนวิธีการทำเงินให้งอกเงย โดยที่เราไม่ต้องทำงานไปตลอดชีวิต
ร่วมเป็นสมาชิก Supporter เพื่อสนับสนุน Blue O’Clock ในการผลิตสื่อการเรียนการศึกษา
https://www.youtube.com/c/blueoclock/join
กระดานซื้อขายแลกเปลี่ยน Bitcoin \u0026 Cryptocurrency
อันดับ 1 ของไทย Bitkub https://www.blueoclock.com/bitkub
อันดับ 1 ของโลก Binance https://www.blueoclock.com/binance
อ่านเวอร์ชั่นบทความ https://www.blueoclock.com/howtomakemoneywithoutworkingrobertkiyosakirichdad/
กดติดตามช่องตรงนี้เลย http://bit.ly/SubscribeBlueoclock
Resources
https://youtu.be/RiAN8TEx7ok
ติดตามพวกเราได้ที่
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/theblueoclock
Website : https://www.blueoclock.com
Academy : http://bit.ly/bocacademy
ติดต่อเรื่องงาน/โฆษณา/สปอนเซอร์/ผลิตวีดีโอ
Email : [email protected]
Facebook : https://m.me/theblueoclock

William Ackman: Everything You Need to Know About Finance and Investing in Under an Hour | Big Think
Everything You Need to Know About Finance and Investing in Under an Hour
Watch the newest video from Big Think: https://bigth.ink/NewVideo
Join Big Think Edge for exclusive videos: https://bigth.ink/Edge
Bill Ackman is one of the top investors in the world, and he’s said that he’s aiming to have \”one of the greatest investment track records of all time.\” As the CEO of Pershing Square Capital Management, the hedge fund he founded, he oversees $19 billion in assets.
But before he became one of the elite, he learned the basics of investing in his early 20s.
This Big Think video is aimed at young professionals just starting out, as well as those who are more experienced but lack a financial background.
Ackman takes viewers through the founding of a lemonade stand to teach the basics, explaining how investors pay for equity, a word interchangeable with \”stock.\” In the example, the owner starts with $750, with $250 of that coming from a loan.
WILLIAM ACKMAN:
William Ackman is founder and CEO of Pershing Square Capital Management. Formed in 2003, the hedgefund has acquired significant shares in companies such as JC Penney, General Growth Properties, Fortune Bands and Kraft Foods. Ackman advocates strategies of \”activist investing,\” the practice of using stock shares in publiclytraded companies to influence management practices in a way that benefits shareholder interests.
TRANSCRIPT:
Hi, I’m Bill Ackman. I’m the CEO of Pershing Square Capital Management and I’m here today to talk to you about everything you need to know about finance and investing and I’m going to get it done in an hour and you’ll be ready to go.
How to Start and Grow a Business
So let’s begin. We’re going to go into business together. We’re going to start a company and we’re going to start a lemonade stand and now I don’t have any money today, so I’m going to have to raise money from investors to launch the business. So how am I going to do that? Well I’m going to form a corporation. That is a little filing that you make with the State and you come up with a name for a business. We’ll call it Bill’s Lemonade Stand and we’re going to raise money from outside investors. We need a little money to get started, so we’re going to start our business with 1,000 shares of stock. We just made up that number and we’re going to sell 500 shares more for a $1 each to an investor. The investor is going to put up $500. We’re going to put up the name and the idea. We’re going to have 1,000 shares. He is going to have 500 shares. He is going to own a third of the business for his $500.
So what is our business worth at the start? Well it’s worth $1,500. We have $500 in the bank plus $1,000 because I came up with the idea for the company. Now I’m going to need a little more than $500, so what am I going to do? I’m going to borrow some money. I’m going to borrow from a friend and he’s going to lend me $250 and we’re going to pay him 10% interest a year for that loan.
Now why do we borrow money instead of just selling more stock? Well by borrowing money we keep more of the stock for ourselves, so if the business is successful we’re going to end up with a bigger percentage of the profits.
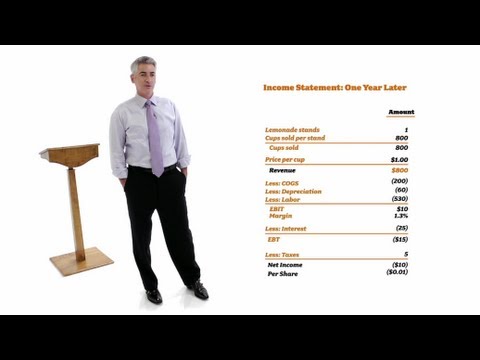
So now we’re going to take a look at what the business looks like on a piece of paper. We’re going to look at something called a balance sheet and a balance sheet tells you where the company stands, what your assets are, what your liabilities are and what your net worth or shareholder equity is. If you take your assets, in this case we’ve raised $500. We also have what is called goodwill because we’ve said the business—in exchange for the $500 the person who put up the money only got a third of the business. The other twothirds is owned by us for starting the company. That is $1,000 of goodwill for the business. We borrowed $250. We’re going to owe $250. That is a liability. So we have $500 in cash from selling stock, $250 from raising debt and we owe a $250 loan and we have a corporation that has, and you’ll see on the chart, shareholders’ equity of $1,500, so that’s our starting point.
Now let’s keep moving. What do we need to do to start our company? We need a lemonade stand. That’s going to cost us about $300. That is called a fixed asset. Unlike lemon or sugar or water this is something like a building that you buy and you build it. It wears out over time, but it’s a fixed asset. And then you need some inventory. What do you need to make lemonade? You need sugar. You need water. You need lemons…
Read the full transcript at https://bigthink.com/videos/learntoinvestandstartabusinessinunderanhour
Balance sheet
Accounting for everyone!

What Is a Balance Sheet? Balance Sheet Definition And Examples
The Balance Sheet helps us to assess the risk of the business. By looking at it you will be able to answer to questions, such as: What is the leverage? Is the company liquid enough?
Remember, leverage means the proportion between equity and debt, while liquidity is the capacity of the business to repay for its shortterm obligations, to run the operations.
Do you want to learn more? Join our course on financial literacy https://biz.fourweekmba.school/p/financialliteracy
The Balance Sheet is comprised of two main sections:
Assets
Liability and Equity
The Assets sections i comprised of:
CURRENT ASSETS:
Cash
Petty Cash
Temporary Investments
Accounts Receivable
Inventory
Join our school at: https://biz.fourweekmba.school/
NON CURRENT ASSETS
Plant, Furniture, Equipment… and so on.
Liabilities are comprised of:
CURRENT LIABILITIES
Accounts Payable
Accrued Expenses
Shortterm loans
NON CURRENT LIABILITIES
Longterm loan
Equity is comprised of:
Owner’s Equity
Retained Earnings
Video transcript:
Hi my name is Grandpa John, I will guide you through the accounting section of the MBA
in pills offered by the four week MBA. for more business educational videos.
check out this link.
we saw in the accounting equation video, that the balance sheet, is divided in two main
sections.
the asset section, and the liability and equity section.
more in detail.
the asset section is comprised of current assets, and non current assets.
main current assets are.
cash, accounts receivable, inventories.
prepaid expenses.
the current assets, are called such, because they are usually on the balance sheet for
one year, or less.
the current assets are usually listed, on the balance sheet, according to their degree
of liquidity.
therefore, cash is the most liquid, while prepaid expenses, the least liquid.cash, is
available at any time.
accounts receivable, sum of money to be received from customers.
inventory, a list of goods to be sold.
prepaid expenses, sum paid in advance.
the noncurrent assets are also called, long term assets.
indeed, those are assets that will stay on the balance sheet for years.
such as plants, equipment, furniture, and so on.
on the other side of the balance sheet, we have, the liabilities and equity.
liabilities, are comprised of current liability and non current liability.
current liabiltiies, stay on the balance sheet, for less than a year.
non current, for more than a year.
Let’s see the main current liabilities.
accounts payable, sum of money not yet paid to suppliers, that will be washed away, once
paid.
accrued expenses, sum of money to be paid in the future, such as, payrolls, or tax the
main non current liability is, long term debt.
such as loans contracted with the bank.
then, the equity.
in this sub section are reported items, such as, owner’s equity, retained profits and other
kind of stocks, issued by the organization.
lets see now few examples.
jim sold $100 worth of clothes.
his customer, Janet, paid with credit card.
therefore, this will generate an account receivable, for $100, on Jim’s balance sheet.
jim, has to pay for utilities.
since it is the first time he set up the account.
he has to pay for $1,000 in advance.
this advanced payment, will be shown as, prepaid expense.
jim, this month, did not sell part of the clothes he bought in the previous month.
the unsold clothes, will become part of his inventories.
then, Jim had to pay $50,000 cash, to renovate the store.
this $50,000 will show on his balance sheet, as building improvement, therefore, a long
term fixed asset.
jim, buys clothes for $1,000, with credit card.
the payment will be processed in 30 days.
this transaction, will generate an account payable, on jim’s balance sheet.
Jim, goes to the bank, to ask for a long term loan.
the bank gives Jim, $50,000. this will generate a bank loan.
showed under long term liability, on Jim’s balance sheet.
after a while.
Jim accepts a new partner, Jasmine.
Jasmine puts $50,000 and becomes equity partner.
this transaction, will show on the balance sheet, as owner’s equity.
in conclusion, the balance sheet, is one of the main financial statements.
it is like an instant picture.
and it helps us to assess how risky a business is.
in fact, when a company is too indebted.
you can see it from the balance sheet.
if liabilities are too much in comparison to equity, this can be very dangerous for
the business.to summarize.
the balance sheet is comprised of two main sections.
it is an instant of the business.
and, allows us to see how risky a business is.
if you liked this video, and you found the topic interesting please live a comment at
these links.
if you would like to learn more, about other topics, contact us.
Grandpa John here.
You just enjoyed the accounting section of the MBA in pills offered by the four week
MBA.

The Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is an important component of the GFS framework. This video explains which stocks are included in the GFS balance sheet and which are not. It also discusses the valuation of those stocks and defines the important balance sheet concepts of, net worth and net financial worth.

นอกจากการดูหัวข้อนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถเข้าถึงบทวิจารณ์ดีๆ อื่นๆ อีกมากมายได้ที่นี่: ดูบทความเพิ่มเติมในหมวดหมู่INVESTMENT
Articles compiled by CASTU. See more articles in category: INVESTMENT


natural viagra alternatives viagra government funding snopes does viagra make you horny