You are viewing this post: Conductive and Sensorineural Hearing Loss Deafness for USMLE | snhl คือ
Table of Contents
Conductive and Sensorineural Hearing Loss Deafness for USMLE
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูความรู้เพิ่มเติมที่นี่
Conductive and Sensorineural Hearing Loss and deafnes for students preparing for the USMLE.
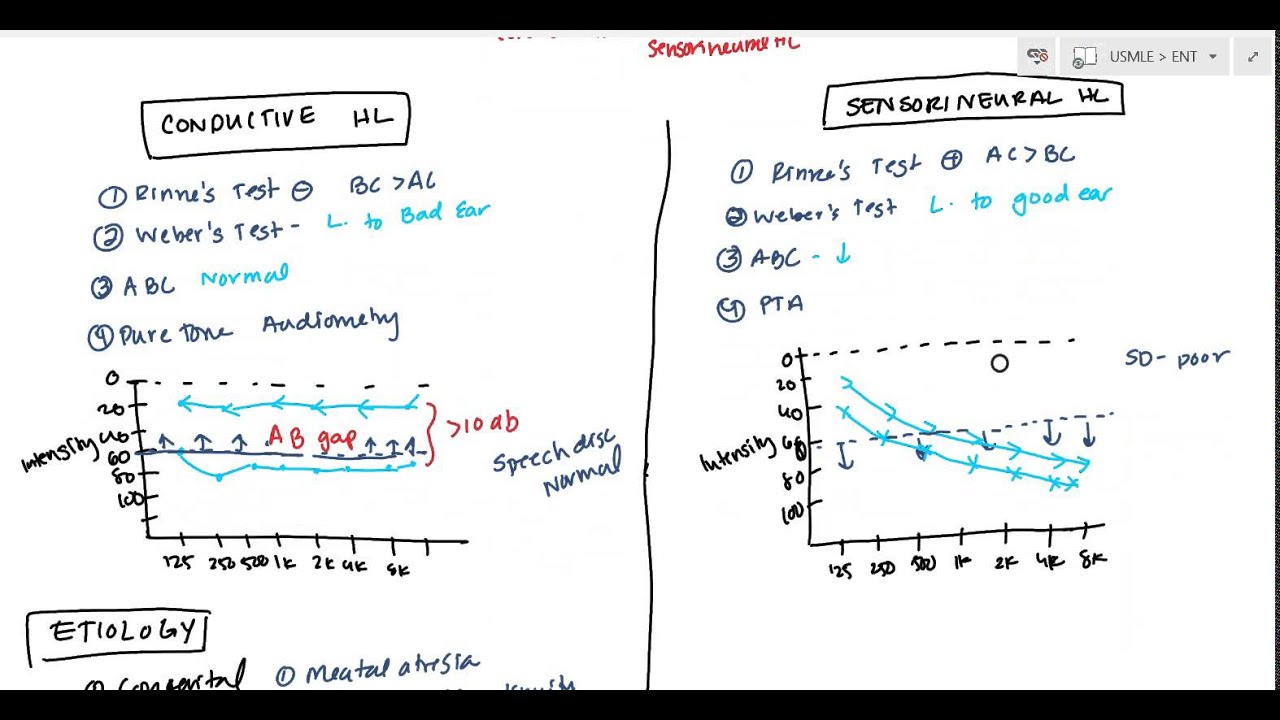
CONDUCTIVE HEARING LOSS DEAFNESS
Conductive hearing loss invovles the part of the ear ranging from stapes to outer ear. Rinne’s Test is negative meaning the bone conduction is greater than air conduction. Weber’s test lateralizes to the bad ear. Absolute bone conduction will be normal. Pure tone audiometry will show normal bone conduction and the air conduction will be lower than 10 decibels known as the AB Gap. Rarely goes below 60 decibels.
Congenital causes include, meatal atresia, ossicular discontinuity, stapes fixation. Acquired causes include obstruction such as ear wax and foriegn body. Tympanic membrane perforation, infection. Ossicle fixation or disruption of the ossicles. Eustuchian tube may also cause.
SENSORINEURAL HEARING LOSS DEAFNESS
Sensorineural hearing loss involves cochlea and cranial nerve 8. Rinne’s test is positive meaning air conduction is greater than bone conduction. Weber’s test lateralizes to the good ear. Absolute bone conduction in sensorineural is decreased. Pure tone audiometry in sensorineural hearing loss will show drop in the higher frequencies and there will not be a large ab gap, but goes below 60 decibels. Speech discrimination will be poor in sensorineural hearing loss.
Acquired causes include labyrinthitis, physical trauma, noise trauma, acoustic neuroma, presbycusis, Meniere’s disease, drugs, systemic diseases (DM, Hypothyroidism), renal syndrome, autoimmune diseases, blood dyscrasias and multiple sclerosis.
Pupillary Light Reflex Test
Check us out on Facebook for DAILY FREE REVIEW QUESTIONS and updates! (https://www.facebook.com/medschoolmadeeasy)
Check out our website for TONS OF FREE REVIEW QUESTIONS!
(http://medschoolmadeeasy.com/)
Thanks for stopping by, and we love hearing from you!
Disclaimer: the information in this video only represents the knowledge and property of the video’s authors no one else.
Weber and Rinne Tests for Conductive or Sensorineural Hearing Loss
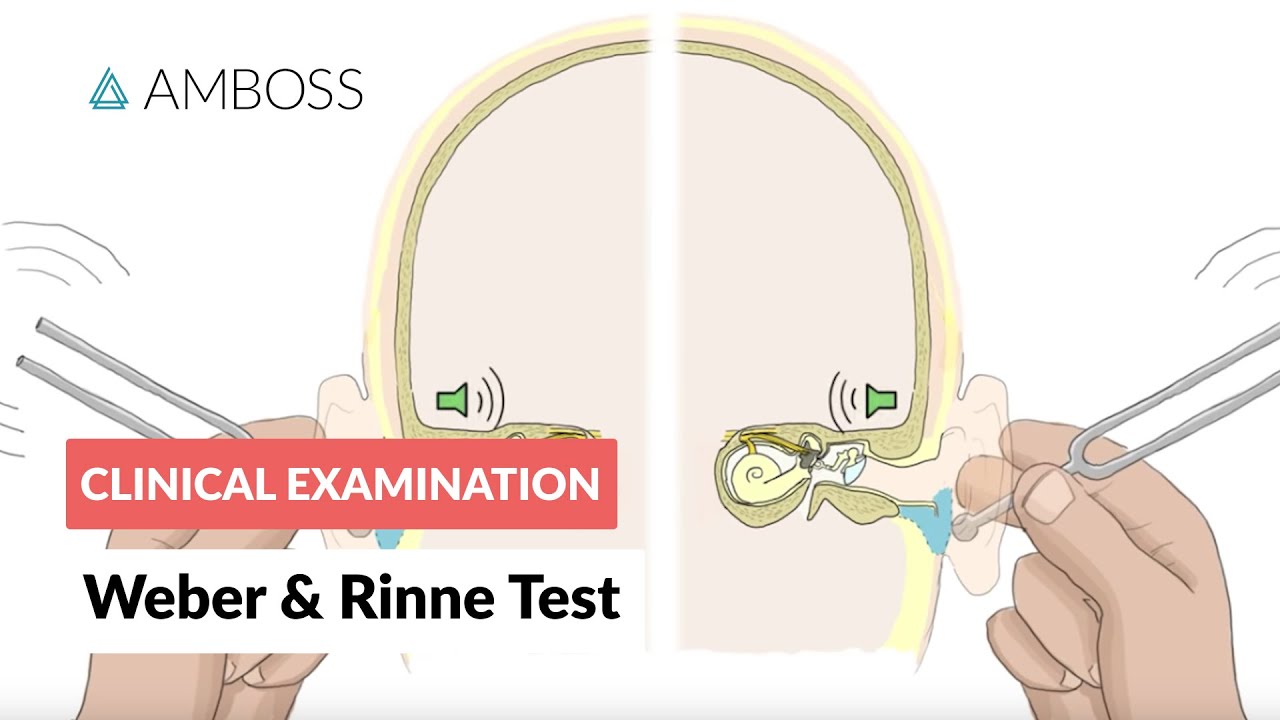
I show how to use a tuning fork for the Rinne test to check if a patient has any conductive hearing loss, and how to perform the Weber test to check whether the patient has any sensorineural hearing loss. Weber test tells you \”weber\” or not a patient can hear something louder on left or right (which would be a positive result indicating sensorineural hearing loss for the ear that is softer). Rinne test tells you if there’s conductive hearing loss if the pt says they hear the sound louder when the fork is directly on their mastoid bone instead of next to their ear this indicates conductive hearing loss.

Weber and Rinne Test – Clinical Examination
The clinical examination of hearing loss should include differentiating between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. There are different causes of sensorineural hearing loss, such as inner ear disease or damage to the cochlear nerve. In all cases, the perception of sound waves via both air and bone conduction is impaired. Sounds reaching the affected ear will therefore be perceived to be quieter than on the unaffected side.
Conductive hearing loss on the other hand is caused by diseases of the middle ear, such as otosclerosis or otitis media. Obstruction of the outer auditory canal, as seen in cerumen impaction, for example, can also lead to conductive hearing loss. In this case, air conduction of sound waves from middle to inner ear is impaired. Bone conduction, however, is unaffected and causes sounds on the affected side to appear louder.
There are two hypotheses that attempt to explain this phenomenon. First, it is assumed that impaired sound conduction causes upregulation of the inner ear, which makes it more sensitive towards stimuli received via bone conduction. It also causes these sounds to be perceived as louder. Second, if sound waves cannot easily reach the inner ear, they probably cannot exit it easily either. These trapped sound waves could therefore make patients perceive sounds as louder.
The Rinne and Weber tests are easy and quick methods for differentiating simple forms of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. More complex illnesses, such as combined conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, often result in test results that are difficult to interpret.
Subscribe to AMBOSS YouTube for the latest clinical examination videos, medical student interviews, study tips and tricks, and live webinars!
Free 5 Day Trial: https://go.amboss.com/ambossYT
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/amboss_med/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/AMBOSS.Med/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/ambossmed
Blog: https://blog.amboss.com/us
AMBOSSMed ClinicalExamination
Vlog Human Language EP 04 : IC คืออะไร?

นอกจากการดูหัวข้อนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถเข้าถึงบทวิจารณ์ดีๆ อื่นๆ อีกมากมายได้ที่นี่: ดูวิธีอื่นๆGENERAL NEWS
Articles compiled by CASTU. See more articles in category: GENERAL NEWS

