You are viewing this post: Vascular Dementia: A Quick Review | vascular dementia คือ
Table of Contents
Vascular Dementia: A Quick Review
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูเพิ่มเติม
While Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia and receives much attention from the public, vascular dementia is the second most common cause of dementia, occurring in between 5% and 10% of all cases of dementia. Vascular dementia is characterized by a decline in cognitive abilities caused by health conditions that either block or reduce blood flow to various regions of the brain, thereby depriving them of needed oxygen and nutrients. Poor blood flow damages and eventually kills brain cells. Some experts prefer using the term “Vascular Cognitive Impairment” rather than vascular dementia, because the cognitive changes that occur can range from mild to severe.
Read More → http://www.drjimcollins.com/vasculardementiaaquickreview/
★ FREE CEU → https://www.ceu.academy/freeceu/
—
CONNECT WITH ME:
Facebook → https://facebook.com/DrJimCollins/
LinkedIn → https://www.linkedin.com/in/DrJimCollins/
Website → http://www.drjimcollins.com

Vascular Dementia Pathology, Animation
(USMLE topics) Also called Vascular Cognitive Impairment: pathology, causes, small vessel disease, risk factors and treatment. This video is available for instant download licensing here : https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com//galleries/narratedvideosbytopics/dementia//medias/07b809dac93543b28c2f42551e4dc06fvasculardementianarratedanimation
Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia
©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved.
Voice by: Ashley Fleming
All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
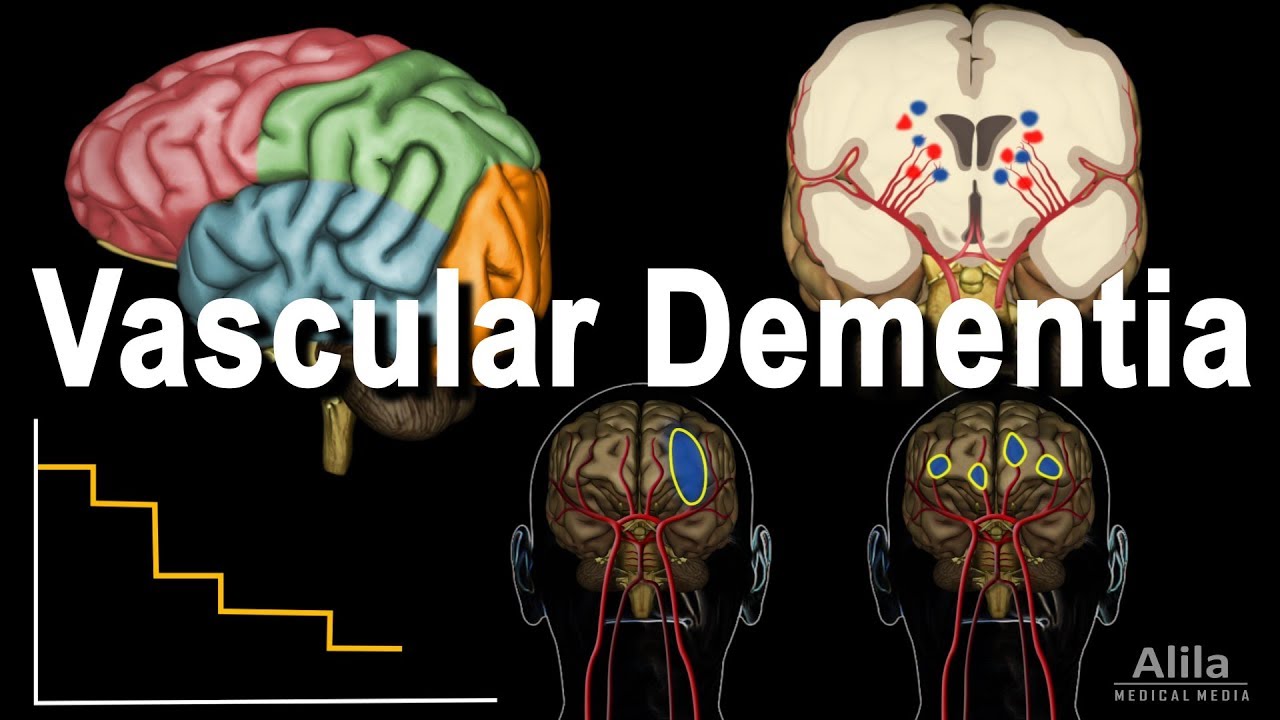
Vascular dementia refers to a group of conditions in which IMPAIRED blood supply to the brain causes neuronal dysfunction, leading to loss of memory and other cognitive abilities. It is the second most common type of dementia, after Alzheimer’s a neurodegenerative disease.
Vascular dementia may develop following a stroke, or a series of ministrokes. A stroke can be ischemic or hemorrhagic. An ischemic stroke happens when a blood clot BLOCKS an artery, interrupting blood flow. Blood clots may form locally, on top of cholesterol plaques as these rupture; or, travel to the brain from the heart, in a condition known as atrial fibrillation, where the heart does not pump properly, blood stagnates and coagulates. Hemorrhagic stroke, on the other hand, occurs when an artery leaks or ruptures. This can result from high blood pressures, overuse of bloodthinners/anticoagulant drugs, or abnormal formations of blood vessels such as aneurysms. As a hemorrhage takes place, brain tissues located BEYOND the site of bleeding are deprived of blood supply. Bleeding also induces contraction of blood vessels, narrowing them and thus further limiting blood flow.
Dementia symptoms may appear SUDDENLY following a SINGLE LARGE stroke, or develop in a STEPWISE fashion as a result of multiple, sometimes unnoticeable, small strokes. Symptoms VARY from person to person depending on the part of the brain that is affected, and may include: problems with memory or thinking skills, confusion, mood changes, speech disorders, impaired balance and movement. The way the symptoms appear can be used to differentiate strokerelated dementia from Alzheimer’s disease, which usually develops GRADUALLY, with specific symptoms appearing in a largely typical order.
But vascular dementia may also progress silently in a CONTINUOUS manner, as a result of agerelated vascular wearandtear, or any conditions that DAMAGE or NARROW blood vessels over time, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes and amyloid deposit. These factors often affect SMALLER blood vessels deep inside the white matter of the brain, causing small blockages and microbleeds that often go UNnoticed to the patients. This is known as “cerebral small vessel disease” and is the most common cause of vascular dementia in older adults.
Another cause of vascular dementia is HYPOperfusion of the entire brain. This may result from heart failures, hypotension, or carotid artery occlusion.
There is no cure for vascular dementia but prevention by controlling vascular risk factors, such as high blood pressures, can be effective. Life style changes such as healthy diets, quitting smoking, and physical exercise have been proven to be beneficial. Treatment is by managing the underlying conditions.
Understanding Vascular Dementia
This Bitesized program takes a deeper dive into understanding Vascular Dementia. For a copy of the slides contact James L. West Center at [email protected] or call 817.877.1199.

Vascular Dementia: Causes \u0026 Prevention
Link to Methods of Prevention: 7:41
Vascular Dementia, or Vascular Cognitive Impairment, is a huge and growing problem, affecting nearly everyone by the age of 70.
Vascular dementia is the result of small blood vessels deep within the brain weakening with old age. The breaking down of these tiny arteries is called Small Vessel Disease. This breaking down of microvasculature is associated with poor blood pressure, but aging itself has been shown to weaken these blood vessels.
There are currently no known cures for vascular dementia, but it has been recently discovered that making simple lifestyle changes may prevent it:
There is a large body of evidence suggesting that physical exercise can dramatically reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
New studies have found that drinking beetroot juice will also dramatically decrease the likelihood of developing vascular cognitive impairment. Beets are high in nitric oxide, which has been shown to improve blood flow and lower blood pressure, thus potentially preventing the breakdown of smaller blood vessels in the brain.
Lastly, a new therapeutic strategy is being developed called Remote Ischemic Conditioning. This approach strengthens an organ over time, such as the brain, by inducing brief cycles of nonlethal ischemia. Since older patients are less willing or less able to exercise, this may be a good alternative.
Peter M. Lawrence, MS
David C. Hess, MD
© 2016 Peter M. Lawrence \u0026 Augusta University, Medical College of Georgia

Medical English: Vascular dementia và nguyên lý chẩn đoán MRI

นอกจากการดูหัวข้อนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถเข้าถึงบทวิจารณ์ดีๆ อื่นๆ อีกมากมายได้ที่นี่: ดูบทความเพิ่มเติมในหมวดหมู่GENERAL NEWS
Articles compiled by CASTU. See more articles in category: GENERAL NEWS

