You are viewing this post: Fractured Neck Of Femur Presented By Martyn Parker | fracture neck of femur คือ
Table of Contents
Fractured Neck Of Femur Presented By Martyn Parker
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูความรู้เพิ่มเติมที่นี่
Martyn Parker is an orthopaedic surgeon with a specialist interest in the treatment of hip fractures.
His job is somewhat unique in that involves the complete care of hip fracture patients from the assessment at the time of admission, through surgery, postoperative care, rehabilitation and subsequent outpatient followup.
He is the author of two textbooks on the management of hip fractures, 18 Cochrane reviews and over 200 journal articles on hip fractures. He has acted as advisor to a number of clinical guidelines on the management of hip fracture in the UK including those from NICE, SIGN and Royal College of Anaesthetists.
Purchase your CPD certificate here: https://bit.ly/3sY1zRx
Subscribe to our YouTube channel and receive updates when a new video is added!
TraumaCare

Neck of femur hip fractures 1 of 2 – Orthopaedics for medical students / finals
Neck of femur hip fractures Orthopaedics for medical students / finals for MBBS PLAB
Made for noncommercial purposes. Images belong to their relevant copyright owners.

Orthopedic in Arabic 33 ( Intracapsular femoral neck fracture , part 1), by Dr.Wahdan
Learn with Dr. Wahdan 2
You can download the lecture from this link
https://docdro.id/602MHgh
Femoral Neck Fracture Classification – Everything You Need To Know – Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes classifications of femoral neck fractures.
Femoral neck fractures can occur as a result of low energy trauma in the elderly. In this case you will need to get a medical consultation! Femoral neck fractures can also occur due to high energy trauma, such as with falls or motor vehicle accidents. Femoral neck fractures can occur in older as well as younger patients, and in these cases you need to apply the ATLS protocol. Femoral neck fractures can also occur due to insufficiency fractures. This occurs due to weak bones, because of osteoporosis or osteopenia. The patient will have groin pain, pain with axial compression and the xray may be normal (helpful in diagnosing insufficiency fracture). There may also be a stress fracture due to overuse and more loading on the hips. Stress fractures may occur in athletes, ballet dancers, or military recruits.
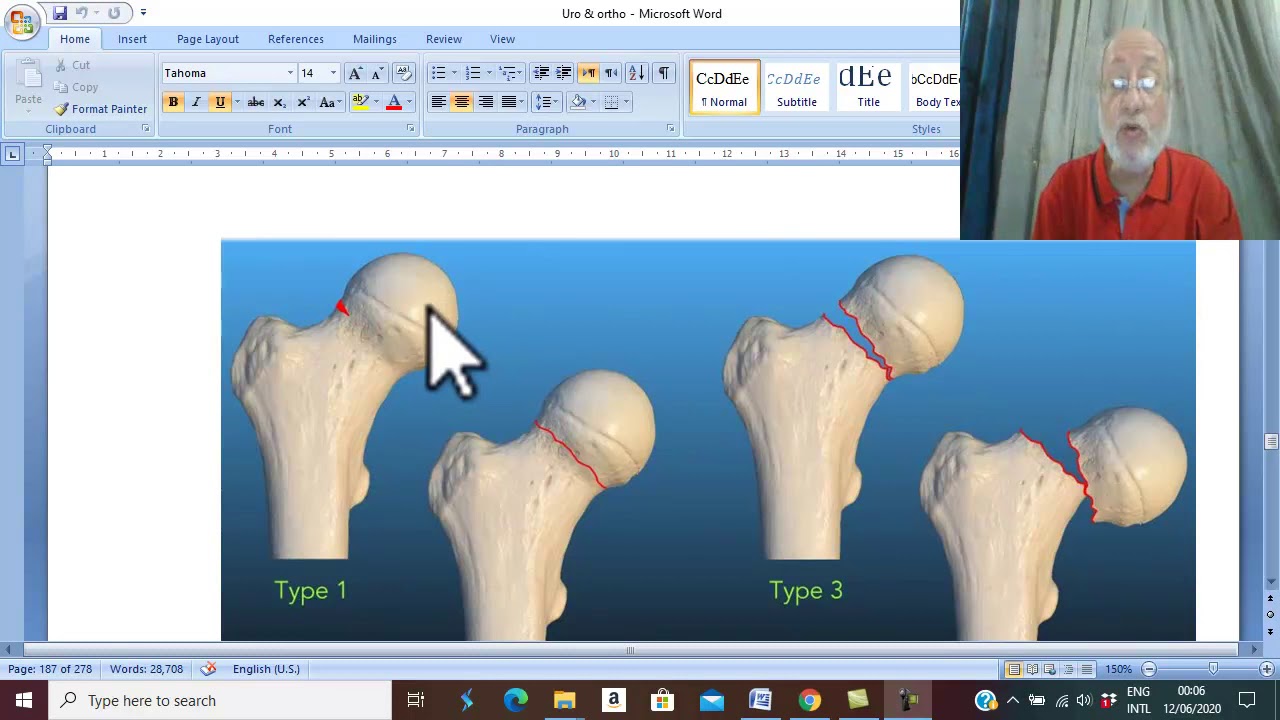
Anatomic classification
1. Subcapital – common
2. Transcervical
3. Basicervical
The subcapital fracture has two classifications: the garden classification and Pauwel’s classification. The garden classification system classifies the fracture according to the amount or degree of displacement. It relates the amount of displacement to the risk of vascular disruption. This classification applies to the geriatric and insufficiency fractures. It can then be classified into two groups: the nondisplaced and the displaced. Types I and II are nondisplaced, while types III and IV are displaced. Type I is incomplete and impacted in valgus. Type II is a complete fracture and nondisplaced on at least two planes (anteroposterior \u0026 lateral). Type III is a complete fracture and partially displaced. The trabecular pattern of the femoral head does not line up with the acetabular trabecular pattern. A type IV fracture is completely displaced with no continuity between the proximal and distal fragments. The trabecular pattern of the femoral head remains parallel with the acetabulum trabecular pattern.
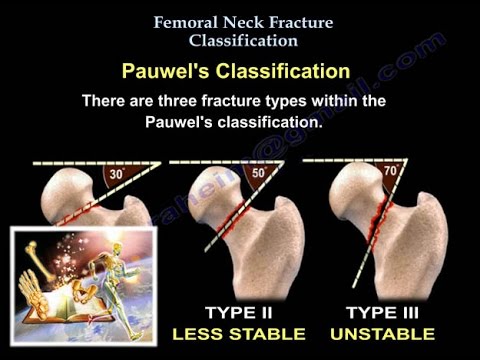
The Pauwel’s Classification is classified into three fracture types. It classifies the fracture according to the orientation and direction of the fracture line across the femoral line. It related to the biomechanical stability. The more vertical the fracture, the more sheer forces and the more the complication rate. Type I is stable and has an obliquity ranging from 030 degrees. Type II is less stable and have an obliquity ranging from 3050 degrees. Lastly, type III is unstable and has an obliquity between 5070 degrees or more. As the fracture progresses from Type I – Type III, the obliquity of the fracture line increases. As the fracture line becomes more vertical, the sheer forces increase and the instability increases. A horizontal fracture is good and stable while a vertical fracture is bad and unstable. The more displaced the fracture, the more disruption of the blood supply and the chance of avascular necrosis and nonunion (can occur in about 25% of displaced fractures). In nonunion occurs in a younger patient, you may help the patient by doing a subtrochanteric osteotomy to reorient the fracture line from vertical to horizontal (will help the fracture healing).
Femoral Neck Fractures Associated with Femoral Shaft Fractures
The typical neck fracture is vertical and nondisplaced. It may require internal rotation view xrays to see this hip fracture (fracture could be missed). Treatment of this fracture is to fix the femoral neck fracture first, followed by the femoral shaft fracture. The usual combination is parallel screws in the femoral neck and a retrograde femoral rod for the fractured femur.
Stress fractures are more common in females due to the female athletic triad. It can be a tension fracture. The fracture or callus is present on the superior aspect of the femoral neck. Adult bone is weak in tension, so stress fracture of the femoral neck needs to be fixed! This should be an emergency operation before the fracture displaces. With compression fractures, the compression or callus is present on the inferior aspect of the femoral neck. It is believed that if the compression fracture is less than 50% across the neck, then the fracture could be stable and you can do protected crutch ambulation. If the fracture is more than 50% across the neck, then the fracture is unstable and you will do an ORIF. Some surgeons fix all stress fractures of the femoral neck. A female runner with groin pain can indicated a stress fracture. Get an MRI, the fracture will probably need to be fixed.
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
Donate to the University of Toledo Foundation Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Endowed Chair Fund:
https://www.utfoundation.org/foundation/home/Give_Online.aspx?sig=29
Neck of Femur Fracture – Orthopedics
Video on symptoms, signs, diagnosis and treatment of femoral neck fracture from the chapter ‘Hip injuries’ in Orthopaedics
Orthopedics Playlist : https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLLywMQWaFPRRgyMUwJSaEdhMUnbtdpE5P
If you need the ppt, please click the join button and become a member 🙂

นอกจากการดูหัวข้อนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถเข้าถึงบทวิจารณ์ดีๆ อื่นๆ อีกมากมายได้ที่นี่: ดูบทความเพิ่มเติมในหมวดหมู่GENERAL NEWS
Articles compiled by CASTU. See more articles in category: GENERAL NEWS

